As cooperation deteriorated, and finally terminated in 1953, it was inevitable that eventually there were some issues with trademarks between the two Zeiss’s. I mean they were on different sides of the Iron Curtain. The East German Carl Zeiss company did not own all the rights to some of the names and brands. This would likely have been fine had they just been sold within the eastern-bloc countries, however many were made to be exported to the west (which is really somewhat ironic) – lenses were developed to sell in the West to produce hard currency. They achieved this at the beginning by resurrecting pre-war designs. Political influence over East Germany did not have any influence in how products were manufactured.

In February 1954 Zeiss in Heidenheim fired the first shots in what would eventually become a worldwide litigation. They obtained an injunction in the District Court of Goettingen to prevent the continued sale of Jena-made, Zeiss-marked goods [1]. In April Zeiss Jena countered in West Germany by seeking an injunction and an order registering the Zeiss marks in West Germany in its name. That action was dismissed in 1960 when the West German Supreme Court ruled that there was no one in the Soviet Zone having capacity to represent the Zeiss Foundation.
In the same year Zeiss Heidenheim brought action against the Zeiss Jena to prevent them from using the Zeiss name and trademarks anywhere in the world. The Supreme Court of the Federal German Republic determined that the Heidenheim firm was entitled to exclusive use of the Zeiss name and trademarks in West Germany and West Berlin [1]. Interestingly, a CIA report from 1954 [2] suggests that should the naming issues take an “unfavourable” turn for VEB CZJ, then the plan was to change its name to VEB Ernst Abbe Werk (which they obviously never did).
There was also a long court battle in the US over who owned the rights to the Zeiss name. The litigation commenced on February 14, 1962, filed by Carl Zeiss Foundation and Zeiss Ikon AG against VEB Carl Zeiss Jena and its US distributors [1] (Carl Zeiss Stiftung v. VEB Carl Zeiss Jena). The case went to discovery from 1963-1967 and finally to trial in November 1967. On November 7, 1968, the court found in favour of the plaintiffs, deciding that the US trademarks “Zeiss”, “Zeiss Ikon”, and “Carl Zeiss Jena”, were the property of the Zeiss firm located in West Germany. As to the legitimacy of this? The courts found that the original “Stiftung” ceased to exist in Jena when it had been stripped of its assets. The Stiftung’s domicile was then changed from Jena to Heidenheim. It was not until 1971 [3] that the US Supreme Court finally settled the case of Carl Zeiss vs. VEB Carl Zeiss Jena, after a long 9½ year battle for control of the “Zeiss” trademark, siding with Heidenheim.

After this, Carl Zeiss marketed their lenses as “Carl Zeiss” exclusively in the United States, whereas Carl Zeiss Jena exported their lenses to the US with the marking “aus Jena”, or sometimes “JENOPTIK”, or even “JENOPTIK JENA”. The branding on these lenses was changed: “T” instead of Tessar, “B” for Biotar, “Bm” for Biometar, “S” for Sonnar, “F” for Flektogon, etc. in order not to infringe on the copyright. Therefore a lens might be labelled “Carl Zeiss Jena s”, or “aus Jena s”, and be exactly the same lens. It really depended on where the lenses were sold.
- In the Eastern-bloc countries, CZJ could use the name “Carl Zeiss”. Carl Zeiss Oberkochen was not allowed to use “Zeiss” by itself, and instead used the name “Opton” or “Zeiss-Opton”.
- In some western countries – namely West Germany, Italy, Greece, Holland, Belgium, Luxembourg, and Austria – CZO was allowed to use the name “Carl Zeiss”. CZJ chose to use the name “aus Jena” in the case of lenses.
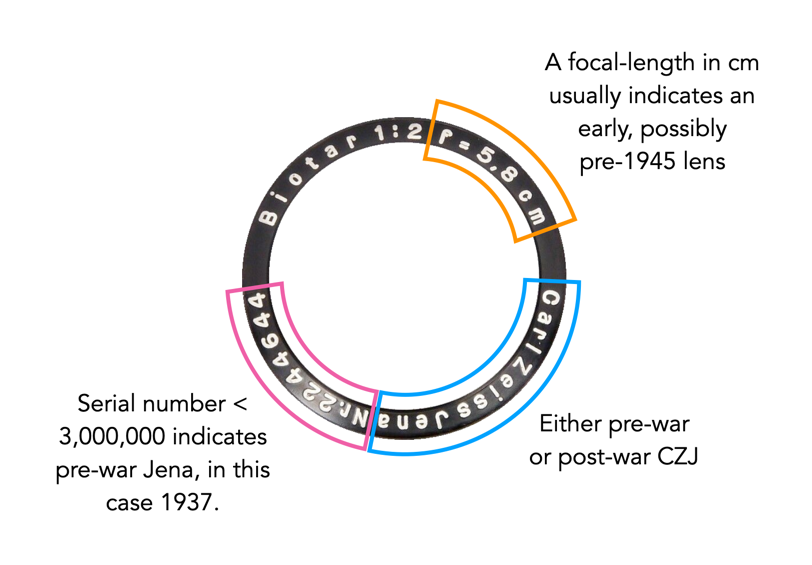
- The rest of the world, i.e. Commonwealth countries like England and Canada, Switzerland, Japan, both companies could use the name “Carl Zeiss”, but only if there was an indicator of origin. For example CZO used “Carl Zeiss West Germany”, and CZJ used “Carl Zeiss Jena” or the term DDR somewhere.

Of course it is also easy to identify a lens if it is marked with DDR. Some lenses were made in only East or West Germany, while others had names which continued to be shared.
- East German only lenses: Biometar (a modified Planar), Flektogon (similar to Distagon), Flexon, Pancolar
- West German only lenses: Distagon
- Shared lenses: Hologon, Biogon, Biotar, Magnar, Planar, Protar, Sonnar, Tessar, Topogon, Triotar
Further reading:
- Shapiro, I., “Zeiss v. Zeiss – The Cold War in a Microcosm”, International Lawyer, 7(2) pp.235-251 (1973)
- “Possible Name Change of VEB Carl Zeiss Jena”, Central Intelligence Agency, Information Report, 22 Nov (1954)
- Allison, R.C., “The Carl Zeiss Case”, International Lawyer, 3(3), pp.525-535 (1969)