Should you buy a camera with an APS-C sensor, or a full-frame?
This argument has been going on for a number of years now, and still divides the photographic community. Is APS-C better than full-frame, or is it sub-optimal? Well, I think it’s all about perspective. APS-C, along with Micro-Four-Thirds are frequently viewed as mere crop-sensors, a designation that only exists because we perpetuate the falsehood that full-frame offers the “standard” sensor size. This stems from the fact that 36×24mm was the standard film size before digital cameras came along. As digital cameras evolved, “full-frame” became the name for the sensor size that matched a 35mm negative.
However we are at the point in time where each sensor size should be considered on its own merits, (and pitfalls) without unnecessary inference that it is a mere “stepping-stone” to a full-frame. Identifying an APS-C sensor, which has a size of 23.6×15.7mm, as “just a crop” sensor does not give the camera the kudos it deserves. The problem lies in every aspect of how these cameras relate to one another, but manifests itself best in lenses.

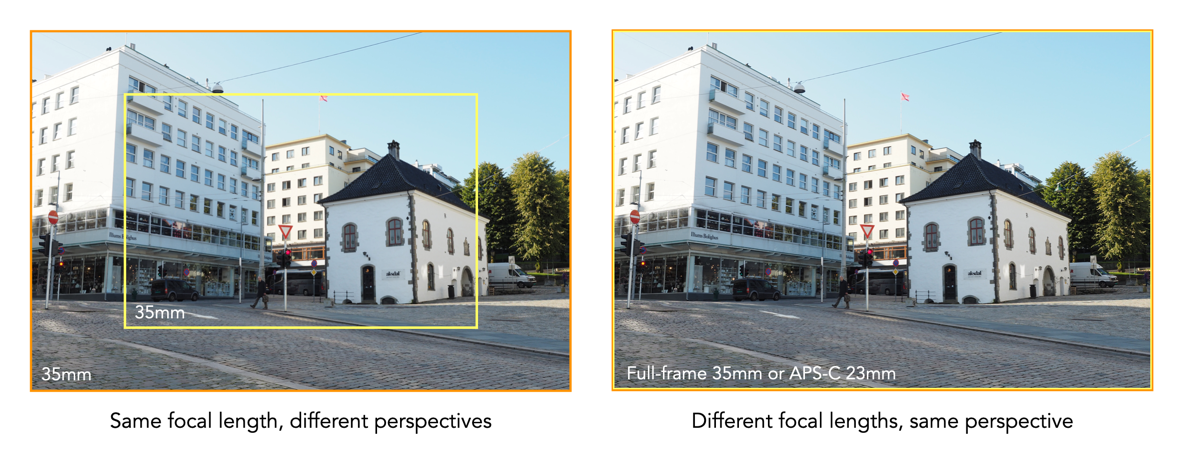
Most APS-C sensors have a crop-factor of 1.5 (except Canon which is 1.6). This means lenses function a little differently than on full-frame lenses. Now a 50mm lens is always 50mm, regardless of the system it is associated with − it’s how that 50mm is interpreted in relation to the sensor that is important. For example a 50mm lens is a “normal” lens for a full-frame camera, while in APS-C land a normal is going to be a lens with a focal length of 33-35mm. A 50mm lens on an APS-C sensor will give a smaller picture than a full-frame, because well obviously the sensor is smaller. So an APS-C 50mm has the same effect as a 75mm lens on a full-frame camera in terms of what is in the picture.
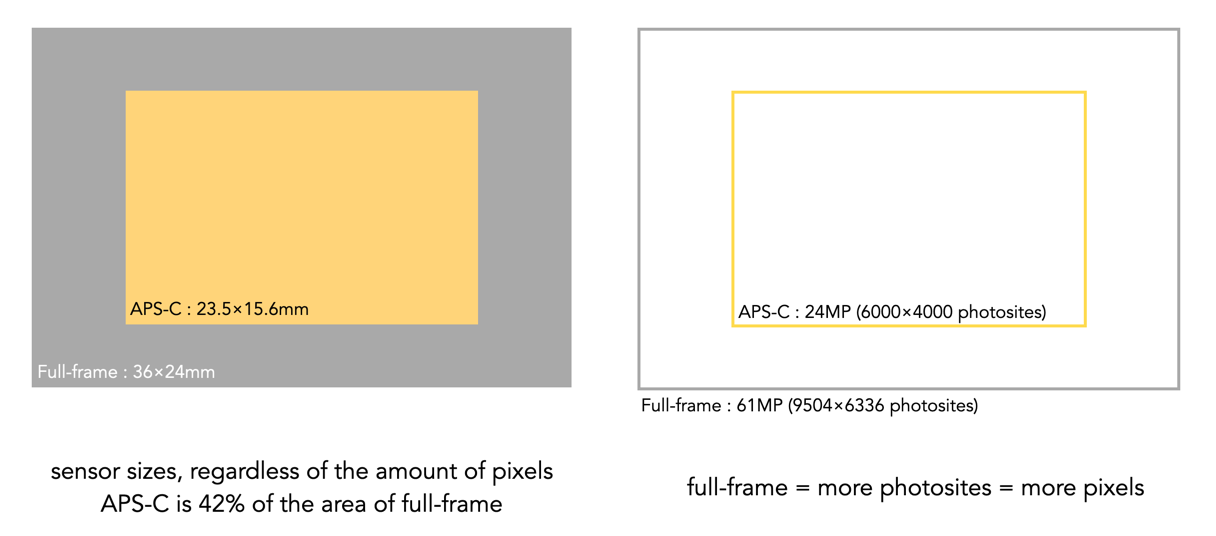
There are obviously things that full-frame sensors do better, and things that APS-C format cameras do better. Image size is the first, which is purely the result of full-frame cameras having more photosites on their sensors. With the evolution of pixel-shifting technology this may be a mute-point as super-resolution images are already available on some systems. Full-frame cameras also tend to have better dynamic range and low-light performance. This is because photosites are often bigger on full-frame cameras, so they can collect more light and better differentiate between light intensities. This means they work better in low-light situations introducing less noise. But digital cameras rely on software to turn the data from photosites into the pixels in an image, and so as software improves, so too will things like noise suppression algorithms in APS-C.

But not every full-frame has larger photosites. For example a Fuji X-H1 camera with a 24MP sensor has 6000×4000 photosites, with a photosite pitch of 3.88μm. The Sony a7CR has a 61MP sensor (9504×6336) with a pixel pitch of 3.73μm, which is actually smaller than that of the APS-C sensor. So more pixels, but perhaps a low-light performance that isn’t that much better. And what is anyone going to do with images 60MP in size? Post them on the web? I think not.
| feature | APS-C | full-frame |
|---|---|---|
| low-light performance | good | excellent |
| depth of field | deeper | more shallow |
| lens availability | large selection | good selection, fewer third-party lenses |
| lens cost | affordable | more expensive |
| portability | light, easy to carry | heavy, bulky |
| dynamic range | slightly reduced | wider |
| applications | street photography, sport, wildlife, travel | low-light, studio, landscapes, portrait |
| camera body cost | typically affordable | usually expensive |
| wide angle lenses | 18-23mm | 28-35mm |
| normal lenses | 26-38mm | 40-58mm |
Full-frame cameras, just like medium-format cameras are for people who need the things they provide – high resolution, low-light abilities, etc. Many people tend to correlate a full-frame camera with high quality because of its sensor size, but quality isn’t necessarily associated with high-resolution images. Yes, more data captured by a camera means more detail in an image, but that doesn’t automatically mean that APS-C sensors (or even MFT) are inferior.
Most non-professional photographers don’t need huge image sizes, just like they don’t need a Leica. APS-C cameras are considerably lighter, and more compact than their full-frame brethren. APS-C lens are also cheaper to purchase, because they are easier to build, and require less glass. In all likelihood there is also a broader ecosystem of third-party lenses for non-full-frame cameras as well, as they are cheaper to manufacture. Over time as newer sensors evolve, APS-C may be well positioned to take a more prominent role in the camera world.
Further reading: