DIP is the Digital Image Processing system. Once the ADC has performed its conversion, each of the values from the photosite has been converted from a voltage to a binary number representing some value in its bit depth. So basically you have a matrix of integers representing each of the original photosites. The problem is that this is essentially a matrix of grayscale values, with each element of the matrix representing with a Red, Green of Blue pixel (basically a RAW image). If a RAW image is required, then no further processing is performed, the RAW image and its associated metadata are saved in a RAW image file format. However to obtain a colour RGB image and store it as a JPEG, further processing must be performed.
First it is necessary to perform a task called demosaicing (or demosaiking, or debayering). Demosaicing separates the red, green, and blue elements of the Bayer image into three distinct R, G, and B components. Note a colouring filtering mechanism other than Bayer may be used. The problem is that each of these layers is sparse – the green layer contains 50% green pixels, and the remainder are empty. The red and blue layers only contain 25% of red and blue pixels respectively. Values for the empty pixels are then determined using some form of interpolation algorithm. The result is an RGB image containing three layers representing red, green and blue components for each pixel in the image.
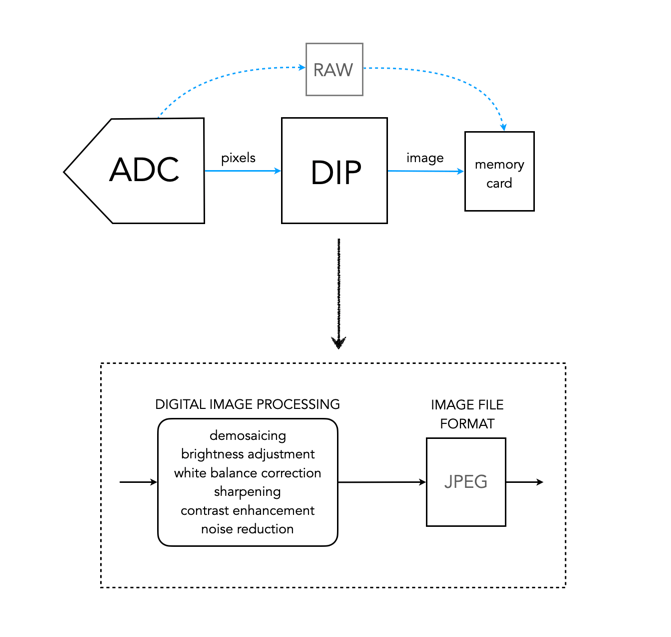
Next any processing related to settings in the camera are performed. For example, the Ricoh GR III has two options for noise reduction: Slow Shutter Speed NR, and High-ISO Noise Reduction. In a typical digital camera there are image processing settings such as grain effect, sharpness, noise reduction, white balance etc. (which don’t affect RAW photos). Some manufacturers also add additional effects such as art effect filters, and film simulations, which are all done within the DIP processor. Finally the RGB image image is processed to allow it to be stored as a JPEG. Some level of compression is applied, and metadata is associated with the image. The JPEG is then stored on the memory card.